Original author: Snow
Original translation: Viper
Article review: Edward, Piccolo, Elisa, Ashley, Joyce
introduction
With the development of blockchain technology, decentralized data availability has become one of the important directions to solve one of the three major problems of blockchain. In this context, projects such as Celestia, EigenLayer, Avail DA and NEAR DA have emerged, trying to solve the scalability and performance problems of blockchain through innovative technologies and designs, thereby promoting the development of the blockchain ecosystem.
Data availability issues
Introduction to Data Availability
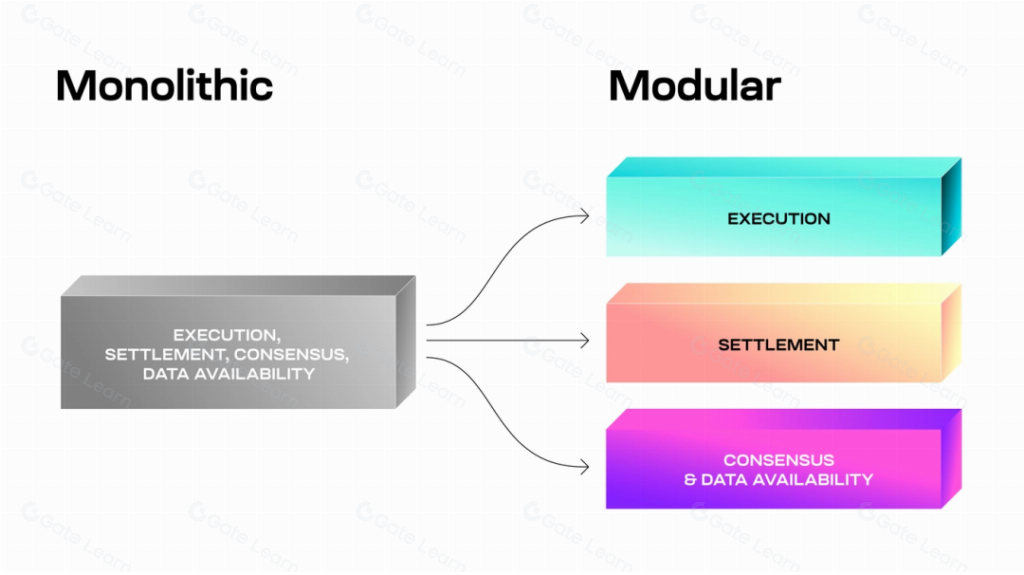
In todays blockchain architecture, data availability (DA) is a crucial component. Unlike traditional single blockchains, modular blockchains decompose the network into different functional layers, including execution, data availability (DA), consensus, and settlement. Among these layers, the data availability (DA) layer is responsible for storing the data required to verify the validity of transactions.
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
Data availability issues
In blockchain and distributed ledger technology, data availability is a critical challenge. At its core, ensuring that all transaction data can be publicly accessed and verified on the network is essential to maintaining the integrity and security of the blockchain system.
In the blockchain system, the transaction data of each block needs to be verified by network nodes. However, ensuring that this data can be reliably distributed to the entire network and guaranteed to be equally accessible to all participants is a key issue.
Why is data availability important?
Off-chain transactions: L2 solutions are designed to process transactions outside the main chain to improve the scalability of the entire system. However, this approach may bring some challenges because L2 does not immediately record all transaction data on the L1 blockchain, which may lead to difficulties in verifying the integrity and accuracy of all transaction data.
Security dependency on Layer 1: Although L2 networks have the ability to operate independently and process transactions, they still rely on L1 networks to ensure overall security. Ensuring complete and accurate data transmission from L2 to L1 is critical to maintaining the integrity of the entire network.
Resolving mechanisms’ reliance on data: L2 networks can apply mechanisms such as fraud proofs to resolve potential disputes. The effectiveness of these mechanisms lies in the availability and accessibility of transaction data.
Transparency and trust issues: In blockchain technology, transparency is a crucial principle. In L2 networks, any issues regarding data availability may lead to a trust crisis, as users may not be able to independently verify the authenticity of transactions.
Increased complexity of verification: The introduction of L2 increases the complexity of ensuring the accuracy of data returned to the main chain, which also brings the risk of data availability issues, thus affecting the reliability of the network.
DA Solutions
There are various solutions for the DA layer, which can be roughly divided into two main types: on-chain and off-chain.
Data availability in L2 solutions is usually addressed in two different ways:
-
On-chain data availability: All transaction data is stored on the L1 chain, which has higher security but also higher costs. This means that L2 still uses Ethereum as the DA layer and relies on Ethereum to reduce the cost of data availability.
-
Off-chain data availability: Data is stored off-chain, and only the summary (hash value) of the encrypted information is stored on-chain. This method is cost-effective, but it requires reliance on external entities to retrieve data. In other words, instead of using Ethereum as a DA layer, more economical methods are found to obtain data availability. Depending on the degree of decentralization and security, off-chain solutions can be divided into four types: Validium, Data Availability Committee (DAC), Volition, and general DA solutions.
DA track project summary
There are relatively few players in the field of data availability (DA). In addition to Ethereum, there are some key projects such as Celestia, Eigenlayer, Avail and Near DA, which have their own characteristics in terms of project progress. In DA projects, factors such as security, customizability, interoperability and cost are crucial.
Celestia
Celestia is the first project to adopt a modular Data Availability (DA) network, designed to scale to the growth of the number of users in a secure manner. Its modular design makes it easy for anyone to launch an independent blockchain.
As a leader in modular public chains, Celestia is developed based on the Cosmos SDK and is committed to improving data availability. On the mainnet, Celestia has achieved significant competitive advantages.
Technical features
Celestia is designed to separate execution, consensus, settlement, and data availability. This modular structure allows for specialization and optimization at each level, improving the overall efficiency and scalability of the network.
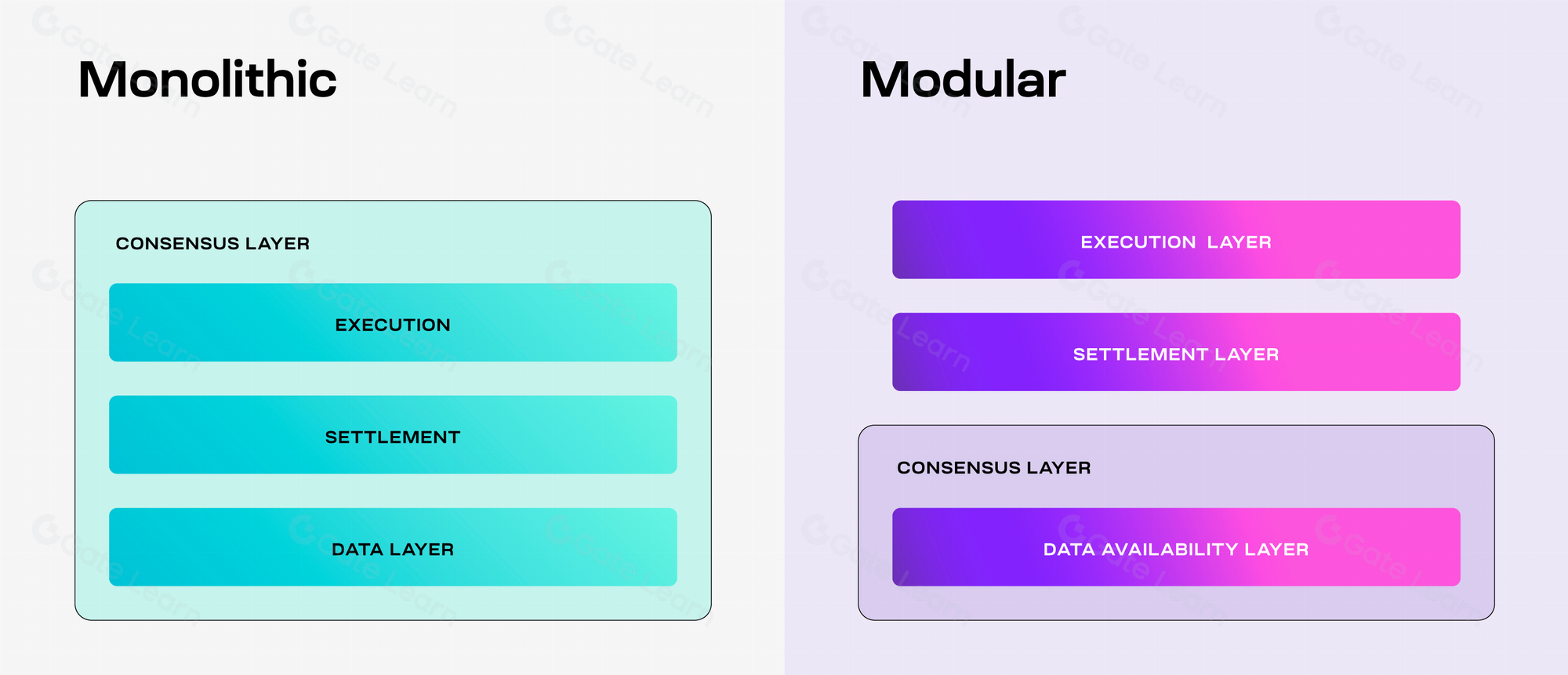
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/monolithic-vs-modular
Data Availability Sampling (DAS)
Data Availability Sampling (DAS) is a method that allows light nodes to verify data availability without downloading the entire block. By randomly sampling data blocks, light nodes can verify whether this data can be successfully retrieved and verified, thereby inferring whether the data of the entire block is available.
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
Namespaced Merkle Trees (NMTs)
NMTs allow blockchain data to be partitioned into separate namespaces for different applications. This means that each application only needs to download and process the data relevant to it, significantly reducing data processing requirements.
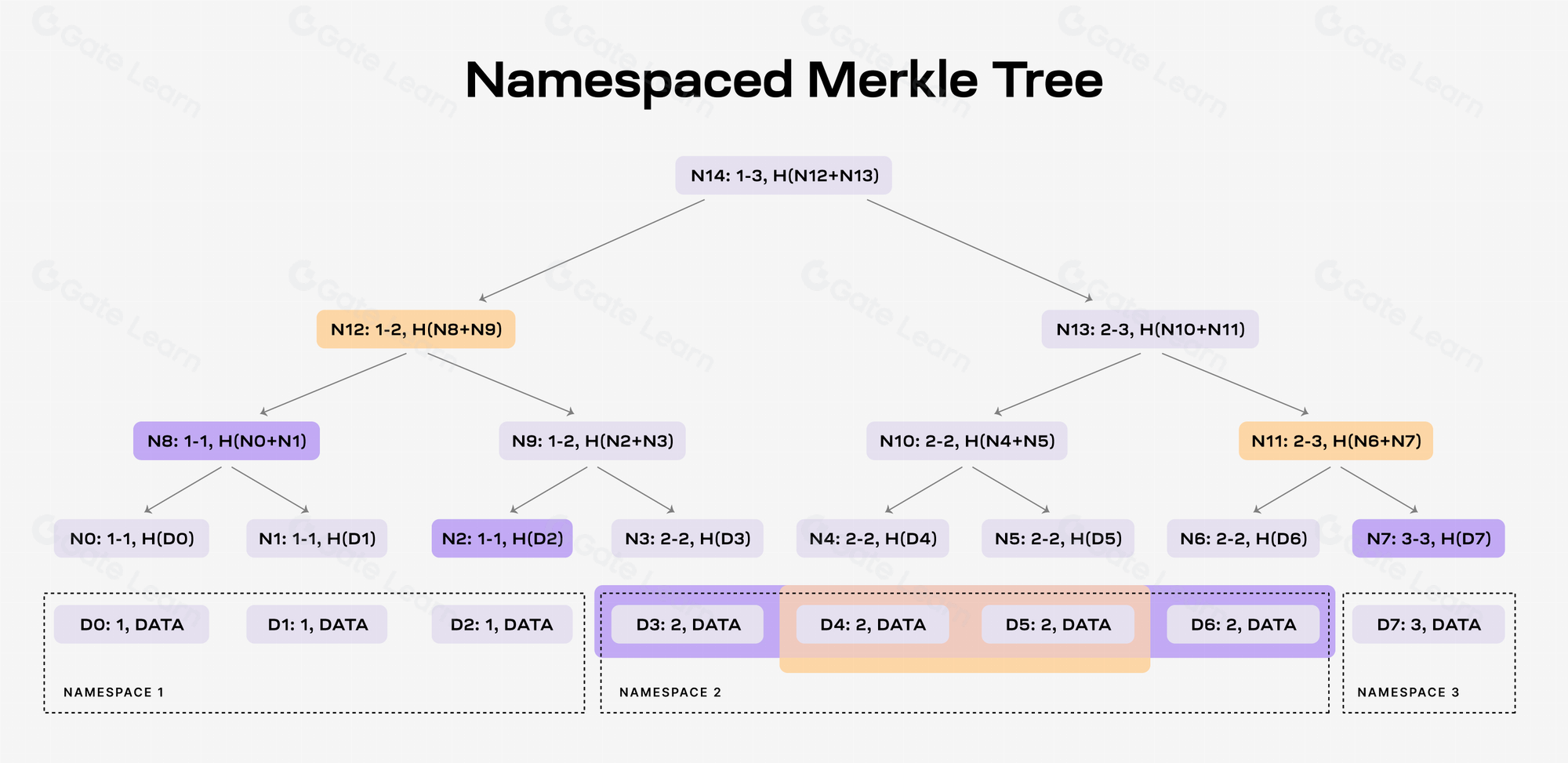
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
Features Analysis
Celestias Rollups are different from Ethereum Rollups in that the way they run on Celestia independently determines the canonical state, and this independence increases the autonomy of nodes. Nodes can freely choose how to operate through soft and hard forks, reducing reliance on centralized governance, thereby promoting more experimentation and innovation.
Celestias Rollups are execution-independent, which means they are not restricted to EVM-compatible designs. This openness provides a wider space for innovation in virtual machines and helps promote the development of technology.
Celestia simplifies the blockchain deployment process. Using tools such as Optimint, developers can quickly deploy new chains without having to worry about the complexity and high costs of consensus mechanisms.
Celestia separates the growth of active state from the storage of historical data, providing a more efficient resource pricing mechanism. This approach reduces the impact of each other between execution environments and improves the user experience.
Celestia’s architecture supports the creation of trust-minimized bridges that enable different chains to securely interconnect, thereby enhancing the security and interoperability of blockchain clusters.
Celestia is the first modularly designed DA network with the primary goal of scaling securely as the number of users grows. With its modular structure, launching an independent blockchain becomes simple. Celestia is expected to play an important role in the blockchain industry with its unique approach and technological innovation. Its focus on solving the challenges facing blockchain, especially scalability issues, while maintaining security and decentralization makes it an important player in the growing blockchain ecosystem.
Eigen DA
EigenLayer is a re-staking protocol that allows users to re-stake ETH, lsdETH, and LP Token on other sidechains, oracles, and receive verification rewards as nodes. Eigen DA is a decentralized data availability (DA) service built on Ethereum, built using EigenLayer Restaking, and will become the first active verification service (AVS) on EigenLayer.
Technical features
Enhanced data availability of Ethereum: Eigen DA uses Blob block data and KZG commitments, and with the help of Cancun upgraded Blob block data and KZG commitments, it enhances the data availability of Ethereum. Node verification is done by Ethereums Validators, and the entire process is completed around Ethereums existing infrastructure.
No autonomous consensus and P2P network: Eigen DA nodes re-collateralize ETH in the EigenLayer contract on Ethereum L1 and become a subset of Ethereum validators. Through custody proof, each operator must periodically calculate and submit the value of a function, which can only be calculated if they have stored all blob blocks assigned to them within the specified storage period. If they prove the blob without calculating this function, anyone with access to its data item can slash the ETH held by the node, thereby ensuring the security and reliability of the network.
EigenLayer consensus mechanism: ETH stakers can choose to verify the Eigen DA network and accept Eigen DA specific slashing conditions. Then act as a POS validator to prove the network status.
Data availability layer: Eigen DA breaks the call data into small blocks and performs erasure coding and KCG polynomial commitments on these blocks to facilitate a system where each node only downloads a small part of the system. Even if half of the nodes leave, it will not affect the system. They can do this because even if some blocks are lost, erasure coding can reconstruct the complete data state, and KZG proofs ensure that the blocks they receive are the same as the blocks claimed by the nodes.
Source: https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/intro-to-eigenda-hyperscale-data-availability-for-rollups/
Features Analysis
Eigen DA nodes are a subset of the re-staking nodes in the EigenLayer network. There is no additional staking cost to become an Eigen DA node.
Existing DA solutions use P2P networks to transfer blobs, where operators receive blobs from their peers and then rebroadcast the same blobs to others. This greatly limits the achievable DA rate. In EigenDA, the disperser sends blobs directly to the operators of EigenDA. By relying on direct communication to disperse data, data propagation is no longer limited by the constraints of consensus protocols and P2P network throughput, thereby shortening communication, network latency, and confirmation time, and increasing data submission speed.
Eigen DA inherits some of the security of Ethereum and has higher security than other DA solutions.
Eigen DA also supports Rollup to flexibly select different pledge token models, erasure code ratios, etc., providing higher flexibility.
Since the final confirmation of Eigen DA depends on the Eigen DA contract on the Ethereum mainnet, the cost of Eigen DA will be significantly higher than other DA solutions in terms of the time overhead of final confirmation.
Eigen DA uses advanced technologies such as erasure coding, KZG commitment, ACeD, and decouples data availability (DA) from consensus, making it perform well in terms of transaction throughput, node load, and DA cost, far exceeding the Ethereum DA solution. Compared with other DA solutions, Eigen DA has lower startup and staking costs, faster network communication and data submission speed, and higher flexibility. Therefore, Eigen DA is expected to become an emerging competitor in the DA market and is expected to carry part of Ethereums DA services.
TNA Protocol

Source: https://tna-btc.com/
TNA Protocol is a Bitcoin asset and security protocol that integrates full-chain domain name asset issuance and DA solutions. Based on in-depth research on Bitcoin data availability, TNA Protocol launched TNA Core, a BLOB-based DA framework that can synchronize status between the Bitcoin mainnet and the second-layer network, and can also be implemented between multiple Bitcoin second-layer networks, and is both secure and economical. TNA Cores solution can be well integrated in major Bitcoin DA solutions, such as Nubit, B Squared, etc., to assist in achieving more efficient data availability.
In addition, TNA Cores DA solution and its fully-chain-issuable domain name asset Tapnames can be closely integrated to directly define the standards for cross-chain interoperability, allowing users to use domain names to seamlessly trade across various networks, with TNA Core providing a security barrier.
The significance of the TNA Protocol narrative upgrade is huge, which is reflected in the dual benefits of the coin price and the product. First, the narrative upgrade and the accompanying new economic model are conducive to TNA Protocol seeking new liquidity and trading scenarios for tokens, which makes the potential price growth opportunities of tokens larger and clearer; through the cross-chain interoperability standards defined by domain names and DA layer solutions, the use scenarios of TNA Protocol-related tokens will also be increased, thereby helping to increase the value of tokens.
Secondly, this narrative upgrade will also bring significant benefits to the product. The new Bitcoin cross-chain interoperability standard will promote the improvement of user experience and the adoption of more second-layer networks, making Tapnames domain names more competitive and attracting more users to participate and use them.
Therefore, this narrative upgrade will not only have a direct positive impact on the community and coin prices, but will also promote product development and the prosperity of the ecosystem, laying a solid foundation for the long-term sustainable development of the entire ecosystem.
Avail DA
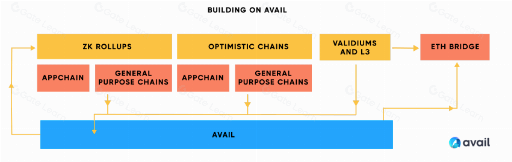
Avail DA is designed to meet the needs of the next generation of trust-minimized applications and sovereign rollups. Its outstanding advantage lies in the use of an innovative security approach that allows light clients to easily verify data availability through peer-to-peer network sampling. With the unparalleled data availability interface and powerful security features provided by Avail DA, developers can create blockchain applications based on zero-knowledge or fraud-proof technology more efficiently and easily.
Source: https://blog.availproject.org/the-avail-vision-reshaping-the-blockchain-landscape/
Avail DA analysis
Avail is a blockchain compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), with features including efficient transaction ordering and recording, and data storage and feasibility verification. Compared with traditional smart contracts and base layer dependencies, Avail allows Rollup to publish data directly to it and verify it through a light client network. This modular design allows developers to store data on Avail and choose other networks for settlement, providing more flexibility and selectivity.
Avails consensus mechanism inherits the BABE and GRANDPA consensus mechanisms of Polkadot SDK, and adopts Polkadots Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS), supporting up to 1,000 verification nodes. In addition to a powerful consensus mechanism, Avail also has decentralized characteristics, sampling data through a light clients P2P network, providing an efficient and reliable backup mechanism to ensure data availability, even in the event of a failure.
Avail excels in transaction ordering, recording, and data feasibility verification, and supports blockchains compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Its light client network verification mechanism allows Rollup on Avail to verify the status through the light client network without relying on smart contracts and the base layer. Due to its modular nature, developers can store data in Avail and choose other networks for settlement.
Node Type
Full nodes: These nodes are responsible for downloading and verifying the correctness of blocks, but do not participate in the consensus process. Their role is critical to ensuring the integrity of the network.
-
Validation nodes: These nodes are at the heart of the Avail DA consensus mechanism. They are responsible for generating blocks, determining the transactions included, and maintaining the order of the network. Validation nodes are incentivized through consensus participation and are the basis for DA layer operations.
-
Light Clients: Operating with limited resources, light clients rely on block headers to participate in the network. They can query full nodes for specific transaction data as needed and are critical to maintaining decentralization and the accessibility of the network.
Near DA
On November 8, 2023, the NEAR Foundation announced the launch of the NEAR Data Availability (NEAR DA) layer, providing powerful and cost-effective data availability for ETH rollup and Ethereum developers. The first users include StarkNets Madara, Caldera, Fluent, Vistara, Dymension RollApps, and Movement Labs.

Source: https://docs.near.org/zh-CN/concepts/basics/protocol
Technology Architecture
NEAR DA leverages an important part of the NEAR consensus mechanism, Nightshade, which parallelizes the network into multiple shards.
Each shard on NEAR produces a small portion of a block, called a chunk. These chunks are aggregated to produce blocks. When a block producer processes a receipt, consensus needs to be reached on the corresponding receipt. Once the block is processed and included in the block, the receipt is no longer needed for consensus and can be removed from the state of the blockchain. Therefore, NEAR will not slow down its consensus in the event of more data than required, but any user of NEAR DA will have ample time to query transaction data. Therefore, scalable and cost-effective data availability is critical for any Rollup solution. As the NEAR protocol moves to stateless validation, it will further reduce the hardware requirements of certain types of validators (block validators). By storing the state in memory, NEAR can support more shards, thereby increasing the decentralization of the system.
advantage analysis
In NEAR DA, consensus validation is provided by NEAR validators who reach consensus when processing blob submissions. In terms of data persistence, full nodes store functional input data for at least three days, while archive nodes can store data for longer periods of time.
The design of NEAR DA ensures efficient use of consensus without wasting too much data. In addition, this data has been indexed by all major browsers on NEAR to provide indexer support.
Finally, with the promise of long-term usability, NEAR DA takes an easy-to-create approach that anyone can build with limited expertise and tools.
The NEAR-Polygon CDK integration allows developers to build their own Rollups and become part of the Polygon ecosystem.
This is the first fusion of NEAR DA with a zero-knowledge based Layer 2 stack, providing more options for developers seeking scalable data availability solutions.
Summarize
In the blockchain field, competition among DA projects such as Celestia, EigenLayer, Avail DA and NEAR DA is fierce. Although DA layer projects have sprung up, their core technologies are not complicated, and each project has its own unique technology and competitive advantages. These projects demonstrate the diversity and innovation in the field of blockchain technology. In the future, as these projects continue to develop and mature, they are expected to make important contributions to the further growth and development of the blockchain ecosystem.
This article is sourced from the internet: Inventory of core projects in the DA track
Original|Odaily Planet Daily Author: Wenser On May 22, the third round of voting for Jupiter Launchpad LFG is about to begin . The candidate projects for this round are the cross-chain interoperability protocol deBridge , the betting platform Divvy.Bet , and the NFT market Exchange Art . Compared with the 5-6 candidate projects in the first two rounds, the number of candidate projects in this round is nearly half of that in the previous two rounds. It is worth noting that based on past voting activities and community feedback, the LFG platform officials have also made some changes to the voting rules to better play the role of the platform. Odaily Planet Daily will introduce the changes in the LFG platform rules in this article and give a brief interpretation.…






